A VPN is one of the greatest methods to secure yourself from data leaks on the internet, particularly if you operate from a regular office, home office, iPhone, or while on the road.
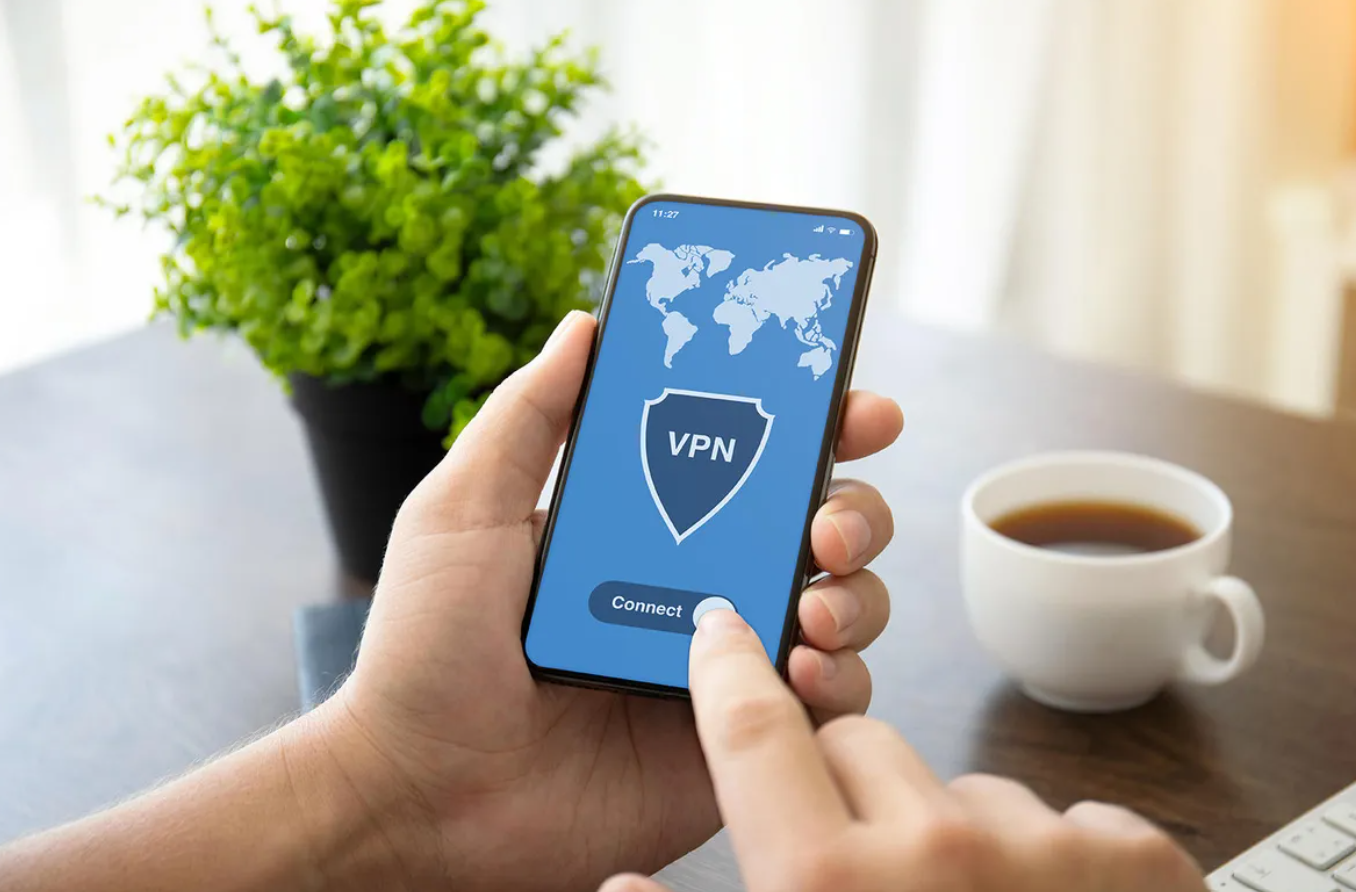

Here we will cover what is Virtual Private Network and how it works?
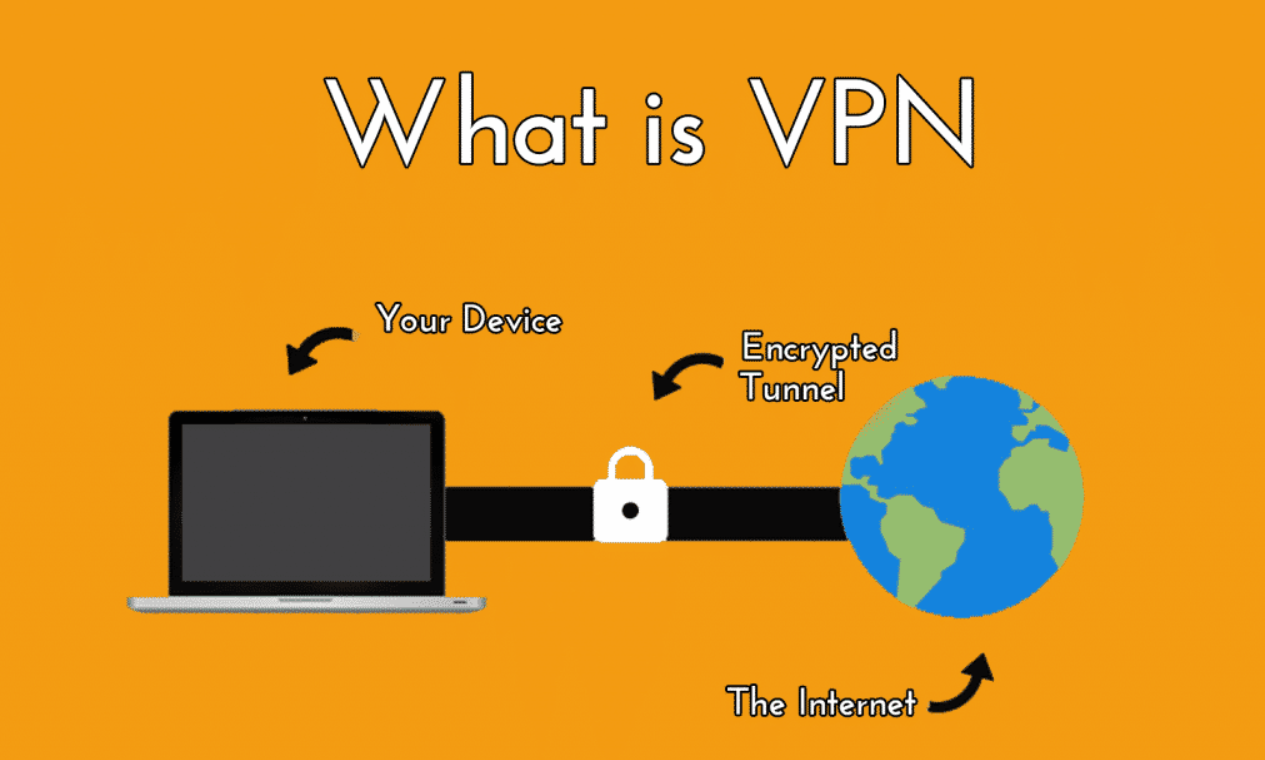
What is VPN?
Virtual Private Network is abbreviated as VPN.
When surfing over the internet, a VPN’s goal is to preserve your security and privacy.
The issue with the internet is as follows: It’s inherently untrustworthy. When the internet was first built, the capacity to send packages (chunks of data) as regularly as possible was a primary concern. Nodes would regularly fall down since networking across the country and throughout the world was still in its infancy. Instead of securing data, most of the internet’s key protocols (communication techniques) were built to route around failure.
Email, surfing, chat, Facebook, and other programs you’re familiar with are all built on top of the IP core. Even though different criteria have been developed, not all internet applications are safe. Many people still email information without any kind of safety or privacy protection.
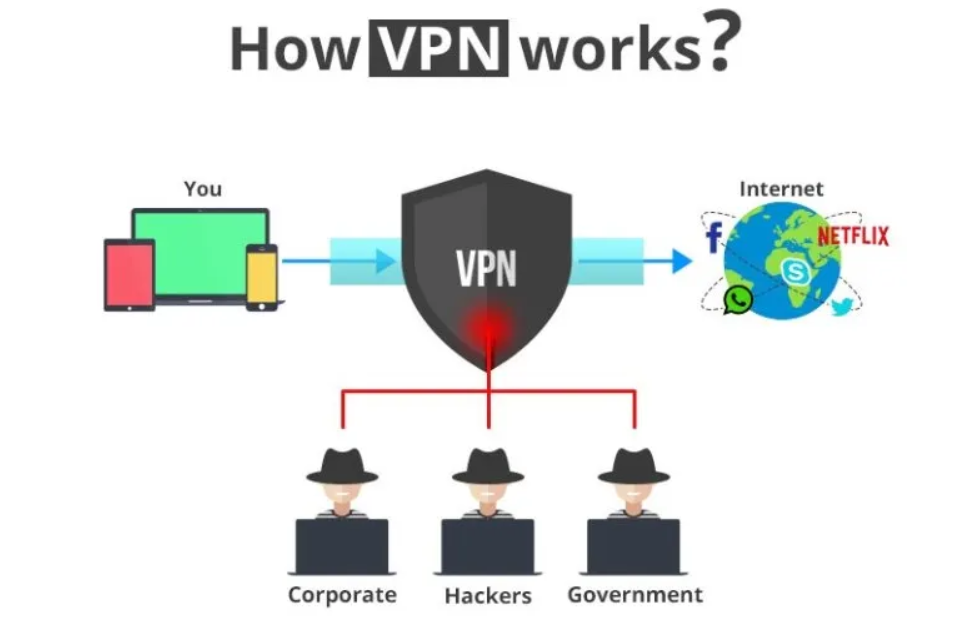
This makes any web user exposed to crooks looking to steal your financial or credit card data, governments looking to spy on their population, as well as other internet users looking to snoop on you for several purposes.
How does a VPN work?
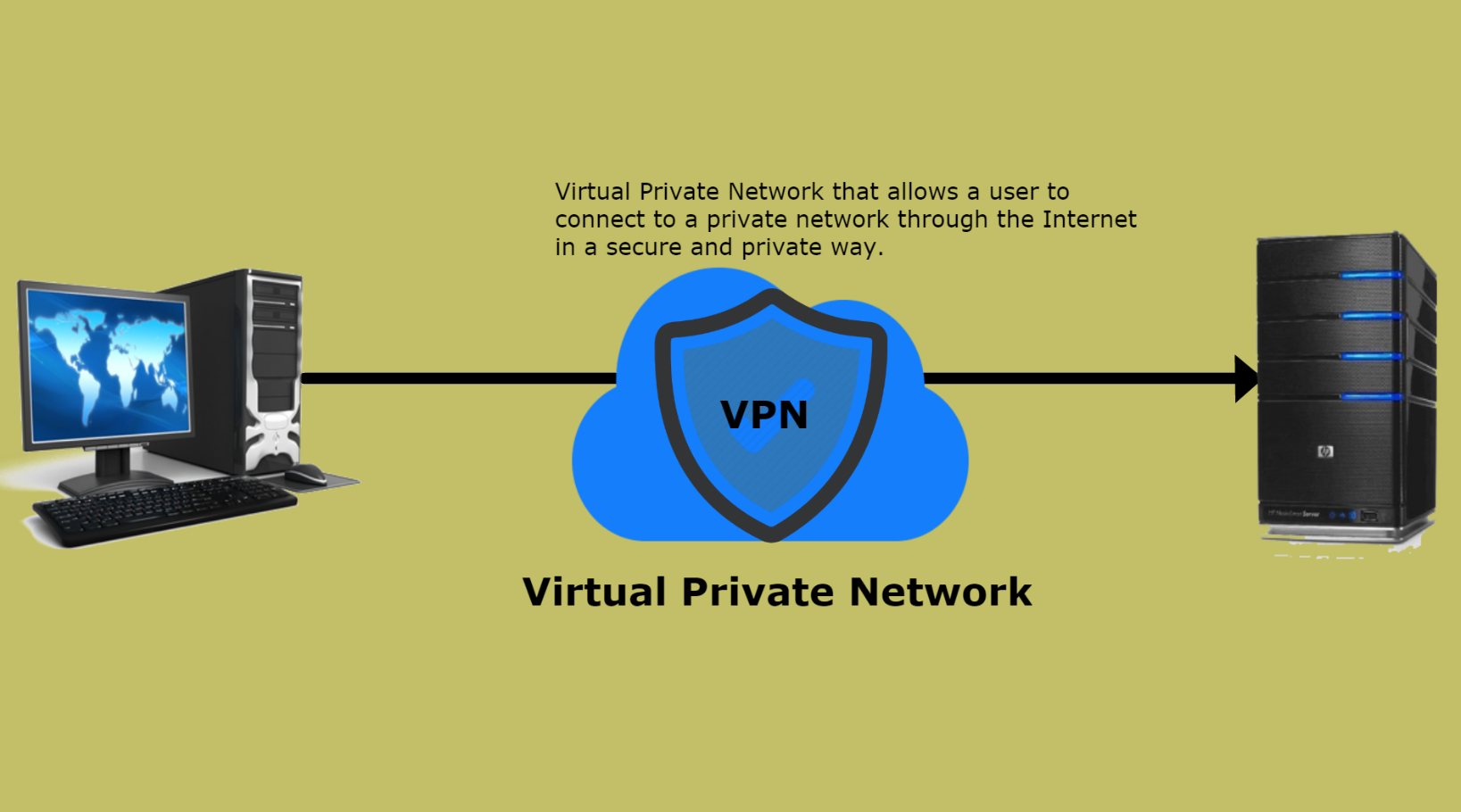
A VPN is a secure connection that is established over the public internet. Everything you transmit is encased and encoded in this secure communication platform, making it difficult to read your packets even if they are stolen. VPNs are crucial and effective tools for protecting yourself and your privacy, but they are not without flaws.
Let’s begin with the fundamental concept of internet connectivity. Assume you’re sitting at your computer and wish to go to a website like ZDNet. To begin a request from your browser is sent to the server which includes a number of messages. If you’re at work, those packets will very definitely pass via switches and routers on your LAN before reaching the public network.
When packets reach the public network, they are forwarded through a number of devices. A second query is sent to a succession of name servers to convert the DNS name ZDNet.com into an IP address. Your web browser receives this information and sends the request to a huge number of computers on the internet.
It eventually hits the ZDNet infrastructure, which likewise routes those packets, fetches a web page (which is made up of several different pieces), and delivers everything back to you.
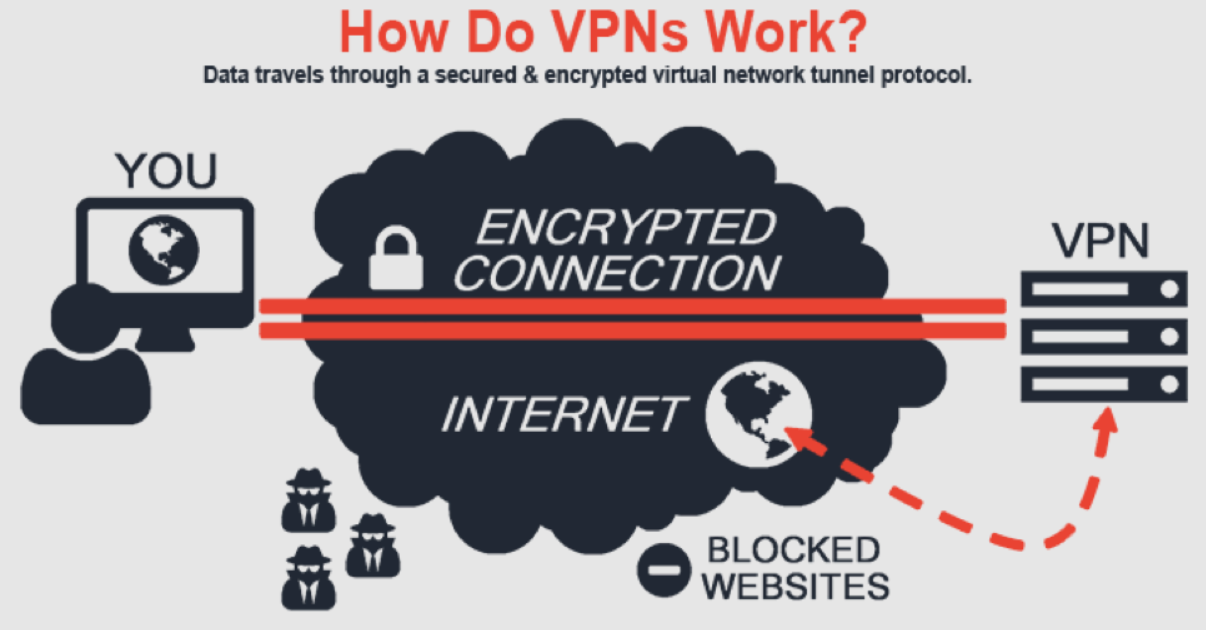
A chain of communication events involving many parties is usually triggered by each internet request. A VPN encrypts such packets at the point of origin, hiding both the contents and information about your originating IP address. The packets are then sent to a VPN server at a faraway location, where they are decrypted, using the VPN application on your computer.
Source: Zdnet
Also read about: How To Check Saved Wi-Fi Password On Computer?